All ASIC testing methodology we discussed so far requires Automatic Test Equipment (ATE). There is a different class of ASIC testing method, called Logic Built-In Self Test (LBIST), whose test pattern data is largely moved off the external ATE, and onto the silicon die itself.
The basic LBIST architecture is shown below:
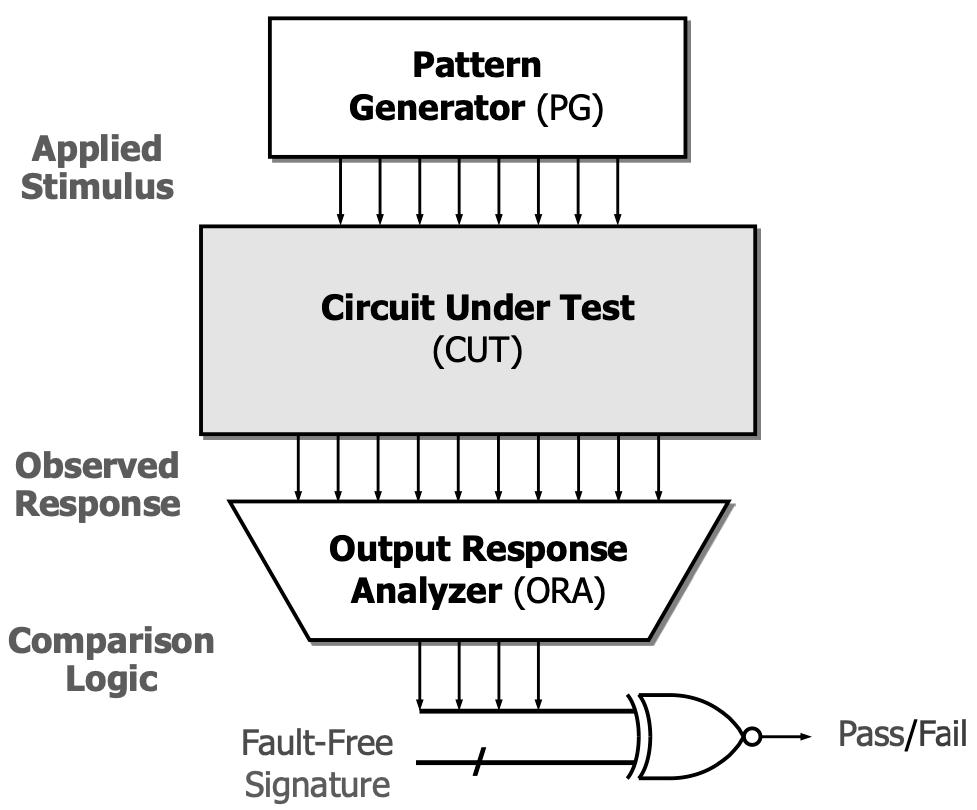
LBIST uses LFSR for random Pattern Generator (PG), and applies this stimulus to the DUT. It then collects and analyzes the responses in Output Response Analyzer (ORA). Since ORA compacts / reduces many response bits to just a few, the “Pass/Fail” result can be false positive.
Clearly, LBIST reduces ATE pattern memory size, and scan chains. Since LBIST runs at chip’s rated speed, the test application time can be reduced as well.
However, LBIST adds overhead logic, including PG, ORA, and the BIST controller. LBIST random pattern yields lower coverage than scan-based insertion, and requires thousands of patterns to achieve coverage.
To learn more, we recommend interviewees to study Chapter 5 of the book “VLSI Test Principles and Architectures: Design for Testability”. It is one of the most comprehensive guides to DFT methodology in the market.


Leave a comment